Category: Class – 5 Science
Force And Energy | Class : 5 | SCIENCE | CBSE / NCERT | Simple Machines | Types of Force |
Measurement | Class : 5 | SCIENCE | CBSE | Measuring Time, Length, Weight, Liquids, Temprature |
Skeleton System and Nervous System | Class – 5 | SCIENCE | CBSE | Human Skeletal and Nervous System |
Volcanoes, Earthquakes, and Tidal Waves| Class: 5 Science | Exercises and Question Answers| CBSE|
Q. Long Answer Type Questions:
1) Describe the three kinds of volcanoes.
Answer = According to the frequency of eruption, volcanoes are of three types: active, dormant, and extinct volcanoes.
- Active volcanoes – These volcanoes can erupt at any time or have erupted in the recent past. many active volcanoes are found around the Pacific Ocean, giving rise to the name the “Pacific Ring of Fire”. Ex: Mount Vesuvius.
- Dormant volcanoes – These volcanoes are those that have not erupted for several years but could erupt in the future. Narcondam in the Andaman Islands is an example of a dormant volcano.
- Extinct volcanoes – These volcanoes are not expected to erupt in the future. some islands have been formed by the eruption of undersea volcanoes. For Ex: The Emperor Seamount chain in the Pacific Ocean.
2) What are the focus, epicenter, and aftershocks?
Answer = The point under the ground where the earthquake begins is called the focus and the corresponding spot on the surface of the Earth is called the epicenter. After the first big quake, smaller quakes or tremors may continue to occur. These are called aftershocks.
3) Mention any three effects of an earthquake.
Answer =
- An earthquake, especially a strong one always causes destruction of property. Buildings may develop cracks or even fall down. Roads and Bridges get damaged.
- An earthquake can also occur under the sea. An undersea earthquake can cause other disasters called tsunamis.
- It can cause landslides and fires.
Our Environment | Class: 5 Science | Exercises and Question Answers| CBSE/ NCERT | Lesson Exercises
Long Answer Type Questions:
1) Describe the different types of pollution.
Answer = There are mainly four types of pollutions. They are as follows:
- Air Pollution – Industries and vehicles are the main sources of air pollution. Burning of garbage also leads to air pollution. It may cause a number of deadly diseases such as Lung cancer and Asthma.
- Water Pollution – Industries is a major source of water pollution. Activities such as washing clothes or bathing animals in rivers also cause water pollution.
- Land Pollution -Land pollution is anything that damages or contaminates the land. Dumping of solid wastes such as plastic bags, glass bottles, and metal containers cause land pollution.
- Noise Pollution – Vehicles and loudspeakers are sources of noise pollution. Exposure to loud noise over a long period of time may even cause deafness.
2) What are the main causes of air and water pollution?
Answer = The main sources of Air pollution are Industries and vehicles. Burning of garbage also leads to air pollution. Industries are also a major source of water pollution. Activities such as washing clothes, bathing animals in rivers also cause water pollution.
3) How is noise pollution harmful to us?
Answer = Vehicles and loudspeakers are sources of noise pollution. Exposure to loud noise over a long period of time may cause deafness.
Light and Shadows| Class : 5 Science | Exercises and Question Answers| CBSE/ NCERT|Lesson Exercises
Q. Long Answer Type Questions.
- What is a shadow? What are the three things needed for a shadow to form?
Answer : The dark spot formed by a translucent or an opaque object when it blocks light is called a shadow. The three things needed for a shadow to form are:
- A Source of light.
- A translucent or an opaque object.
- A surface on which the shadow can be formed.
—————————————————————
2. Write down the features of a shadow.
Answer =A shadow has the following feature.
- A shadow is formed on the opposite side of the light source.
- A shadow is black even when the object is of any other colour.
- A shadow shows only the shape or outline of the object, not the details.
- The size of a shadow depends on the distance between the object and the source of light. It also depends on the distance between the object and the surface where it is formed.
For Objectives and Exercises, click the link given below:
Animals: Habitat & Adaptation || Class 5 – Science ||| CBSE / NCERT || Adaptation in Animals
Earth, Sun, and Moon| Class : 5 Science | Exercises & Question Answers| CBSE/ NCERT|Lesson Exercises
Q. Long Answer Type Questions:
- How is the Earth different from all the other planets in the solar system? Answer = The Earth is different from all other planets in the solar system. It has water, air, and soil. There is a blanket of air around the Earth, called the atmosphere, which protects it from the harmful ultraviolet rays of the sun. The surface of the Earth has various features such as oceans, rivers, mountains, and valleys. ——————–
- Describe the surface of the moon. Answer = The surface of the moon is dry and dusty and is covered with craters, mountains, and valleys. Craters are formed when solid bodies called meteorites crash into the moon’s surface. The oldest craters were formed billions of years ago. there is no air or water on the moon. The moon also has gravity with which it pulls all objects towards its centre. ——————–
- Write a short note on the sun. Answer = The sun is the star that is closest to the Earth, about 150 million kilometers away. It is a huge ball of hot, burning gases. The sun has a thin layers of atmosphere called the corona. It is this corona that we sometimes see during a solar eclipse. The sun is made up of mainly hydrogen and a gas called helium. ——————–
- Write a short note on the “landing on the moon”. Answer = The first men to land on the moon were the crew of the American Space Mission, Apollo 11. It was launched from the Kennedy Space Center at Florida, on July 16, 1969. The rocket that carried it into space was Saturn 5. Apollo 11 carried three American astronauts – Neil Armstrong, Edwin Aldrin, and Michael Collins. Niel Armstrong became the first man to set foot on the moon on July20, 1969. They collected rock samples and bring back to the Earth. These rocks has given scientists a lot of information about the moon. ——————–
- Describe the Lunar eclipse. Answer = When the Earth comes between the Sun and the moon, it blocks a lot of the sunlight from reaching the moon and creates a shadow. This is called an eclipse of the moon or lunar eclipse. Lunar eclipse may be partial or total. During a partial lunar eclipse, only a part of the moon can be seen. During a total lunar eclipse, the moon cannot be seen at all.

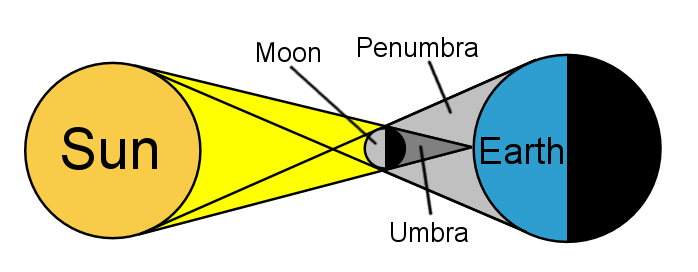
6. Describe how the solar eclipse occurs. Answer = When the moon comes between the Earth and the sun, it blocks some parts of the sun and creates a shadow. The sun looks as though it has a disc in front of it that creates a shadow. This is called a solar eclipse. Solar eclipse may be partial or totall. During a partial solar eclipse, a part of the sun can be seen. During a total solar eclipse, the sun cannot be seen at all.
Rocks and Minerals ~ Class – 5 Science | CBSE / NCERT | Types of Rocks ~ Lesson Explanation
Q. Long Answer Questions.
- Name the different types of igneous rocks. Describe any two.
- How are sedimentary rocks formed? Name the different types of sedimentary rocks. Describe any one.
- What are the different types of metamorphic rocks? Describe any two.
- Describe the various uses of minerals.
Answers:
- Answer = The different types of igneous rocks are : Granite, Obsidian and Pumice. Granite: It is very hard and is formed by the slow cooling of lava. It is used extensively as a building material. Granite comes in many colours and patterns. Obsidian : It is smooth and glassy and is formed by the quick cooling of lava. Obsidian is used in making jewellery and ornaments. It is usually black or dark coloured. ———————————————————————————————————————————
- Answer = Sedimentary rocks are formed by the repeated deposition of rock particles that are worn away from mountains by wind and water. The different types of sedimentary rocks are: Sandstone, Conglomerate, Shale and Limestone. Sandstone: It is a soft stone that is formed of sand particles deposited close together. many of India’s famous old buildings such as, Red Fort in Delhi are made of sandstone. —————————————————————————————————————————————
- Answer = The different types of metamorphic rocks are: Marble, Slate, Gneiss and Quartzite. a) Marble : It is formed from sedimentary rock, limestone. Marble is used in making statues and for other ornamental purposes. b) Slate: It is formed from shale, a sedimentary rock. Like shale, it splits into flat layers. It is used in making bricks and cement. —————————————————————————————————————————
- Answer = We use minerals in different forms in our daily life. some of them are given below: Minerals are used as building material – Certain minerals, such as gypsum and calcite are used to make building material such as mortar, cement , and concrete. Minerals give us useful metals – several minerals are rich in metals. for ex: magnetite is rich in iron, and bauxite is rich in aluminium. they are called ores. These ores are used to extract metals which are further used for making utensils, machine parts etc. Minerals are used as gemstones – several minerals such as diamond, ruby, emerald, sapphire, and topaz are used as gemstones. Minerals serve as fertilizers – some minerals such as sulphates and nitrates are added as fertilizers to the soil. Minerals serve as a part of our diet – Our body needs calcium, sodium, and iron, in small quatities, for healthy growth.
To know the answers of Objectives and Short Answer type questions, watch below video link:


You must be logged in to post a comment.